Understanding Childhood Schizophrenia: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Childhood schizophrenia is a rare and severe mental health disorder that affects children under the age of 13. This condition is estimated to affect fewer than 1 in 10,000 children worldwide. Despite its rarity, childhood schizophrenia is a serious concern with long-lasting and potentially devastating consequences for the affected child.
This article will explore the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for childhood schizophrenia, providing valuable information that can help parents and caregivers better respond to this often-challenging condition.
Symptoms of Childhood Schizophrenia
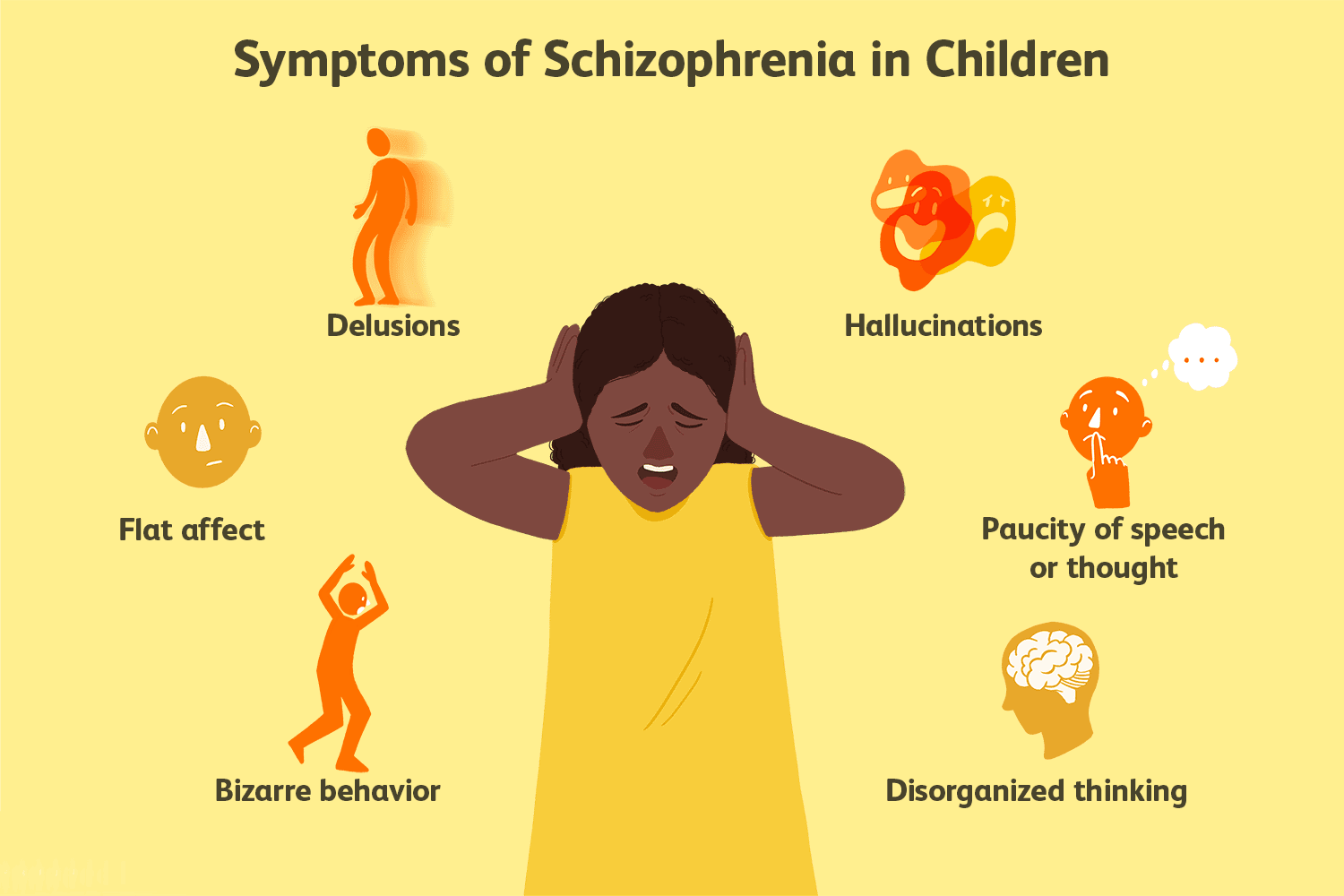
Childhood schizophrenia is characterized by symptoms similar to those of adult schizophrenia. These include delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech and behavior, and a lack of emotional expression. Children with schizophrenia may also experience poor school performance, social isolation, and a decline in daily functioning.
It’s important to note that many of these symptoms may also occur in other childhood disorders, such as autism, depression, and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Therefore, the diagnosis of childhood schizophrenia involves a detailed evaluation by a mental health professional.
Schizophrenia is a complex, chronic mental disorder that affects an individual’s ability to think, behave and express emotions. Its signs and symptoms can manifest in many ways, including delusions, hallucinations, or disorganized speech. These symptoms can make it difficult to function on a day-to-day basis and can be deeply disabling for those who suffer from them. Despite the challenges of living with schizophrenia, various treatments are available to help manage the disorder and improve the quality of life for individuals and their loved ones.
Schizophrenia is a condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It is a serious and misunderstood illness marked by many symptoms, including hallucinations, delusions, and disordered thinking and behavior. While it can occur at any age, in most individuals with schizophrenia, symptoms typically begin in the mid-to late-20s, with some cases starting as late as the mid-30s. Early onset schizophrenia, however, is defined as having symptoms before 18, which is a much rarer occurrence. The onset of schizophrenia before age 13 is sporadic, providing unique challenges for diagnosis and treatment. It is important for individuals who suspect they may be experiencing symptoms of schizophrenia to seek help from a mental healthcare provider as soon as possible.
Schizophrenia is a complex and challenging mental disorder that can be difficult to recognize, especially in its early phases. One of the reasons why is that symptoms can vary significantly in type and severity over time, making it tricky to identify. In some cases, periods of worsening and remission of symptoms are common, while in others, certain symptoms may be present consistently. The unique nature of this disorder is why it is essential to seek professional support if you or a loved one have concerns about possible symptoms, as early diagnosis and treatment can greatly improve outcomes.
Early signs and symptoms
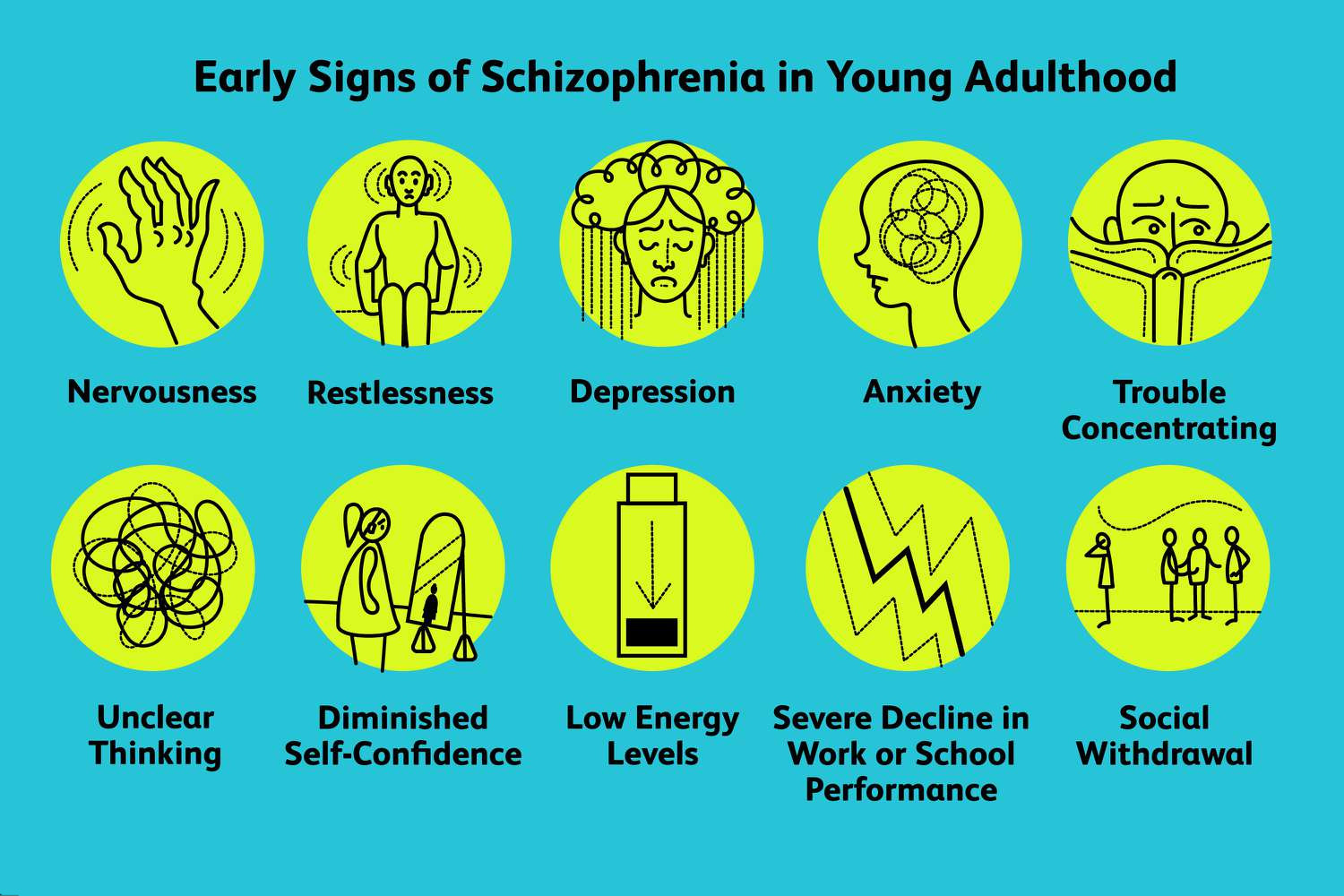
Schizophrenia signs and symptoms in children and teenagers are similar to those in adults, but the condition may be more difficult to recognize in this age group.
Early signs and symptoms may include problems with thinking, behavior, and emotions.
Thinking:
Problems with thinking and reasoning:
Schizophrenia, a severe mental disorder, can affect those afflicted’s thinking and reasoning abilities. People experiencing the symptoms of this disorder can find it difficult to differentiate between what is real and what is not. For them, being unable to filter out sensory stimuli can make it challenging to organize their thoughts and make logical sense of their surroundings. Additionally, sudden mood swings and delusions can further complicate the thought process. Unfortunately, schizophrenia can severely impact a person’s quality of life, making it hard to maintain healthy relationships and hold down a job. Seeking treatment and management options from a mental health professional can help those with schizophrenia improve their thinking abilities and live fulfilling lives.
Bizarre ideas or speech:
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. One common condition symptom is delusions – bizarre beliefs not based on reality. Those with schizophrenia may also experience hallucinations or seeing or hearing things that are not there. It is important to note that these symptoms are not the person’s choice or fault. Rather, they result from biological and environmental factors affecting their brain. It is crucial to provide individuals with schizophrenia with supportive care and treatment to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Confusing dreams or television for reality:
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder that causes a person to experience a distorted perception of reality. One of the symptoms of schizophrenia is the inability to differentiate between what is real and what is not. This often leads to the individual confusing their dreams or hallucinations with reality. In addition, some individuals may also mistake what they see on television as reality, leading to further confusion. It is important to understand that these experiences are not voluntary and can be incredibly distressing for the individual. Seeking professional help and support is crucial for those suffering from schizophrenia to manage their symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
Behavior:
Withdrawal from friends and family:
Schizophrenia is a complex mental disorder that affects a person’s thoughts, perceptions, and behavior. One of the most common symptoms of schizophrenia is social withdrawal, which occurs when people with this condition begin to avoid social interactions with friends and family. The reasons behind this behavior are varied and may include feeling paranoid or fearful, experiencing hallucinations or delusions, or feeling overwhelmed by sensory stimuli. When someone with schizophrenia withdraws from those around them, it can be challenging for their loved ones. It’s important to remember that social withdrawal is a symptom of the illness, not a personal choice. People with schizophrenia require empathy, understanding, and support from their friends and family during this difficult time.
Trouble sleeping:
Schizophrenia is a disorder that affects a person’s ability to think, feel, and behave clearly. One of the common symptoms of schizophrenia is behavior that can make it difficult to sleep. This can include hallucinations, delusions, paranoia, and anxiety, making relaxing and falling asleep hard. Sometimes, the medication used to treat schizophrenia can also make sleeping difficult. People with schizophrenia and their caregivers need to work with healthcare professionals to manage these symptoms and find ways to promote better sleep. This may include developing a consistent sleep routine, practicing relaxation techniques, and potentially adjusting medication as needed. With the right support, people with schizophrenia can improve their sleep and overall quality of life.
Lack of motivation — for example, showing up as a drop in performance at school:
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder that can significantly impact behavior and motivation. A common symptom of the condition is a lack of motivation, which can manifest in various ways, such as a drop in school performance. For individuals with schizophrenia, getting out of bed and completing daily tasks can be a monumental challenge. This lack of drive can make it difficult for them to stay engaged in academic pursuits, resulting in lower grades or even dropping out of school. It’s important to understand that the lack of motivation experienced by those with schizophrenia is not a choice but a consequence of their illness. With appropriate treatment and support, many individuals with schizophrenia can learn coping strategies and find ways to overcome this significant barrier to success.
Not meeting daily expectations, such as bathing or dressing:
Schizophrenia is a chronic mental health disorder characterized by delusions, hallucinations, thought disorders, and abnormal behavior. People with schizophrenia often struggle with daily tasks such as bathing, dressing, and organizing their living space. These struggles are not due to laziness or lack of motivation but rather a symptom of the disorder itself. Schizophrenia affects a person’s ability to reason and organize their thoughts, which makes it difficult for them to meet the expectations of daily life. It’s essential to understand that behaviors associated with schizophrenia are not a choice but are instead a part of the illness. With proper treatment, including medication and therapy, people with schizophrenia can manage their symptoms and work towards meeting daily expectations.
Bizarre behavior:
Schizophrenia is a severe mental disorder that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. This disorder is known to cause delusions, hallucinations, and disordered thinking, which can lead to bizarre behavior. Often, people with schizophrenia become isolated from their friends and families due to their unusual and unpredictable actions. Some may exhibit bizarre gestures and facial expressions. In contrast, others talk incoherently, using nonsensical words and phrases, and understanding that these behaviors are not intentional or voluntary, but a manifestation of mental illness is crucial. People with schizophrenia require proper medical care, therapy, and support from their loved ones to manage their condition and lead fulfilling lives.
Causes of Childhood Schizophrenia
The exact cause of childhood schizophrenia is unclear, but experts believe it may result from genetic and environmental factors. Research has shown that children with a family history of schizophrenia are likelier to develop the condition. Additionally, prenatal and perinatal complications such as maternal infections or birth complications have been linked with an increased risk for schizophrenia.
However, it’s important to remember that not all children with these risk factors will develop schizophrenia, and not all children with schizophrenia have these risk factors.
Risk factors
Although the precise cause of schizophrenia isn’t known, certain factors seem to increase the risk of developing or triggering schizophrenia, including:
- Having a family history of schizophrenia
- Improved immune system activation, such as from inflammation
- Older age of the father
- Some pregnancy and birth complications, such as malnutrition or exposure to toxins or viruses, may impact brain development
- Taking mind-altering (psychoactive) drugs during teen years
Complications
Left untreated, childhood schizophrenia can result in severe emotional, behavioral, and health problems. Complications associated with schizophrenia may occur in childhood or later, such as:
- Suicide, suicide attempts, and thoughts of suicide
- Self-injury
- Anxiety disorders, panic disorders, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
- Depression
- Abuse of alcohol or other drugs, including nicotine
- Family conflicts
- Inability to live independently, attend school, or work
- Social isolation
- Health and medical problems
- Being victimized
- Legal and financial issues and homelessness
- Aggressive behavior, although uncommon
Treatment Options for Childhood Schizophrenia
Psychotherapy, medication, and family education and support are the primary treatment options for childhood schizophrenia. Antipsychotic medications are commonly prescribed to reduce the severity of symptoms. However, these medications may cause side effects such as weight gain, sedation, and tremors.
Additionally, children with schizophrenia may benefit from psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral or family therapy, which can help address their emotional and behavioral difficulties. Family education and support can also benefit the child and their loved ones, providing them with the tools to manage the condition’s symptoms.
Childhood schizophrenia is a complex and challenging condition that requires early detection, accurate diagnosis, and effective treatment to help affected children reach their full potential. Parents and caregivers must be aware of this condition’s symptoms, causes, and treatment options to support their child’s healthy development and well-being. If you suspect your child may have schizophrenia, seek the help of a qualified mental health professional who can offer the necessary support and guidance. With the right intervention and ongoing support, children with schizophrenia can lead fulfilling and meaningful lives.
Contact us today at 816.819.5166 or schedule your appointment online.