Causes and Symptoms of Teen Schizoaffective Disorder
What is Teen Schizoaffective Disorder?
Teen schizoaffective disorder is a rare but serious mental illness that affects teenagers. This disorder is characterized by abnormal thought processes, unpredictable emotions, and the presence of both depression and schizophrenia. This article post will discuss what teen schizoaffective disorder is, its causes, and available treatments.
What are the Symptoms of Teen Schizoaffective Disorder?
Teen schizoaffective disorder can manifest in a variety of ways. Some common symptoms include disorganized thinking and speech; hallucinations; delusions; obsessive-compulsive behaviors; difficulty concentrating or staying focused; memory problems; rapid mood swings; feelings of sadness, worthlessness, and guilt; extreme energy levels or fatigue; difficulty sleeping or oversleeping; changes in appetite or weight gain/loss. It’s important to note that these symptoms vary from person to person and may differ for each individual.
What Causes Teen Schizoaffective Disorder?
The exact cause of the teen schizoaffective disorder is unknown. However, research has suggested that genetic factors may play a role in its development and environmental influences such as trauma or stressors during adolescence. Additionally, hormonal imbalances have been linked to an increased risk of developing this condition.
How Can I Treat Teen Schizoaffective Disorder?
Treatment for teen schizoaffective disorder typically involves a combination of therapy and medication. Psychotherapy is often used to help teens manage their symptoms and work through their feelings related to the diagnosis. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) can be beneficial in changing negative thought patterns associated with this condition. Additionally, antipsychotics can help reduce psychotic symptoms, while antidepressants can help alleviate depressive symptoms, including low moods and suicidal thoughts. It would be best if you spoke with your doctor about all available treatment options for your child’s specific needs.
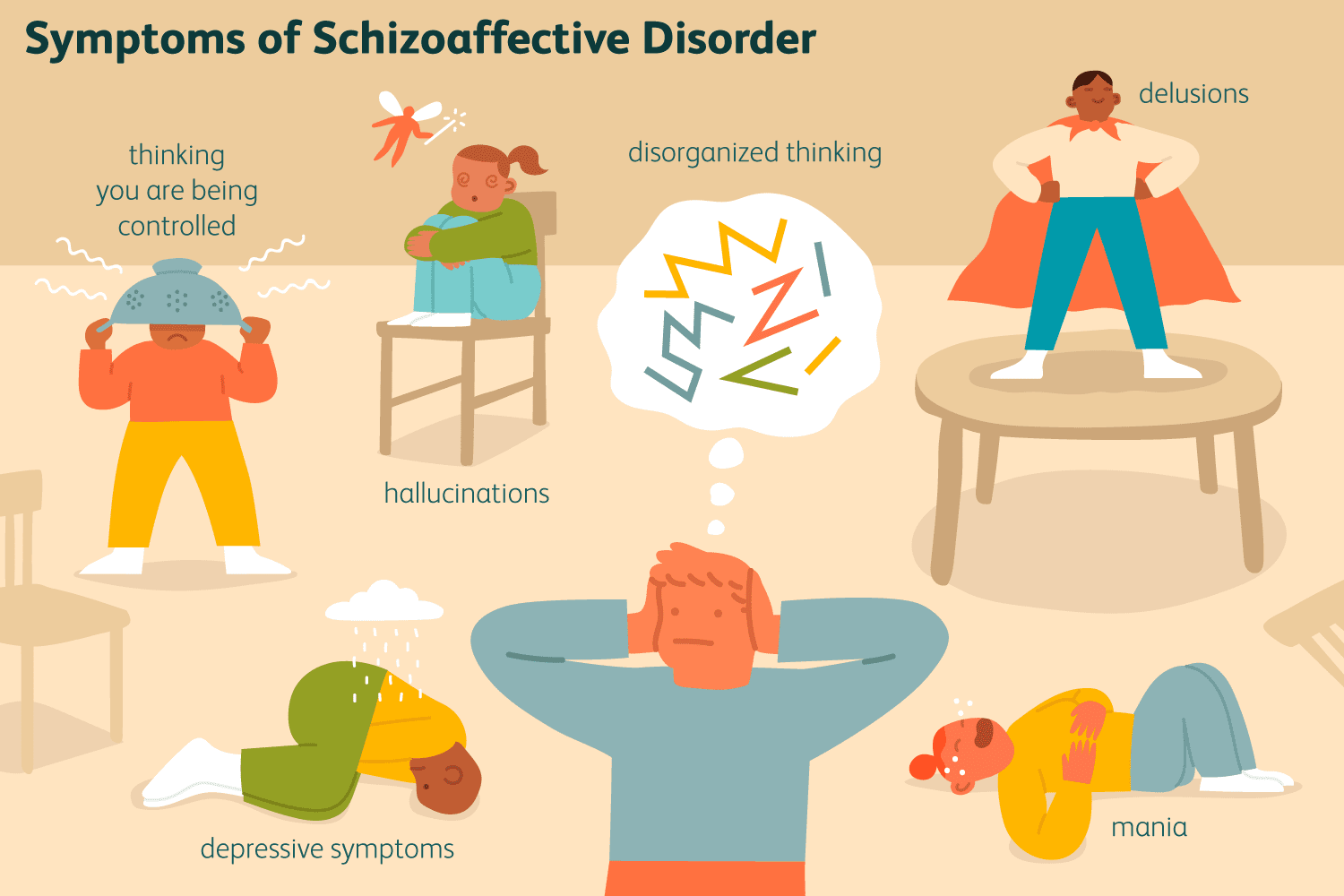
Symptoms of Teen Schizoaffective Disorder
Delusions
A delusion is a false belief that is held despite evidence to the contrary. People with schizophrenia may have paranoid delusions, such as believing that others are out to get them or that they are being watched.
Hallucinations
A hallucination is a false sensory perception, such as hearing voices or seeing things that are not there. People with schizophrenia may experience visual hallucinations, auditory hallucinations, or both.
Disorganized thinking
Disorganized thinking is characterized by a lack of logical flow and coherence in one’s thoughts. This can make it difficult for people with schizophrenia to carry on a conversation or complete tasks.
Disorganized speech
Disorganized speech is characterized by a disruption in the flow of thought, making it difficult for people with schizophrenia to communicate their ideas. This may manifest as tangentiality, derailment, or word salad.
Negative symptoms
Negative symptoms refer to a loss or decrease in normal functioning, such as social withdrawal, apathy, and poverty of speech. People with schizophrenia may appear emotionless or flat due to their negative symptoms.
Catatonia
Catatonia is a state of motor immobility and behavioral abnormality. People with Catatonia may maintain bizarre postures or exhibit repetitive movements for long periods.
Inappropriate affect
Inappropriate affect refers to an inappropriate display of emotions, such as laughing at something that is not funny or crying at something that is not sad. This can be confusing and off-putting for those around the individual with schizophrenia.
Poor hygiene
Poor hygiene is often seen in people with schizophrenia due to neglectful self-care habits. This can lead to problems such as skin infections, body odor, and dental decay.
Social isolation
Social isolation is common among people with schizophrenia due to the illness’s nature and its negative symptoms. This can make it difficult for people with schizophrenia to maintain relationships and participate in activities they enjoy.
Causes of Teen Schizoaffective Disorder
Genetics
One of the most significant risk factors for developing the schizoaffective disorder is genetics. If a person has a first-degree relative, such as a parent or sibling, with the disorder, their risk of developing it increases. Additionally, genetic mutations have been linked to an increased risk of schizoaffective disorder.
Brain Structure
Certain abnormalities in brain structure have also been linked to an increased risk of schizoaffective disorder. For example, people with the schizoaffective disorder often have enlarged ventricles and cavities in the brain that contain cerebrospinal fluid. Additionally, people with the schizoaffective disorder often have reduced gray matter volume in the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain.
Neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters are chemicals that allow communication between nerve cells in the brain. Imbalances in certain neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and serotonin, have been linked to an increased risk of schizoaffective disorder.
Infections
Infections during pregnancy or early childhood have also been linked to an increased risk of schizoaffective disorder. For example, mothers who contract influenza during pregnancy are more likely to have a child with schizoaffective disorder. Children who experience viral infections, such as meningitis or encephalitis, are also at an increased risk of developing the disorder.
Substance Abuse
People who abuse drugs or alcohol are also at an increased risk for developing the schizoaffective disorder. Substance abuse can cause changes in brain chemistry that may lead to psychotic symptoms. Additionally, people who abuse substances are often more likely to experience trauma, another risk factor for developing schizoaffective disorder.
Trauma
Traumatic experiences, such as physical or sexual abuse, can also increase a person’s risk of developing the schizoaffective disorder. Trauma can cause changes in brain chemistry and structure that may lead to the development of psychotic symptoms
Teen schizoaffective disorder is a severe mental health condition that affects teens worldwide. It is characterized by disorganized thinking, unpredictable emotions, and schizophrenia and depression in individuals aged 13-18. While the exact cause of this condition remains unknown, research suggests that genetics, environmental influences such as trauma or stressors during adolescence, and hormonal imbalances may increase risk factors for developing this condition in some individuals. Treatment typically involves psychotherapy combined with medication to help manage symptoms associated with teenage schizoaffective disorder, including hallucinations, delusions, low moods, or suicidal thoughts. For more information on how best to support your teen if diagnosed with this condition, speak with your doctor about all available treatment options for your child’s unique needs today!
Contact us today at 816.819.5166 or schedule your appointment online.